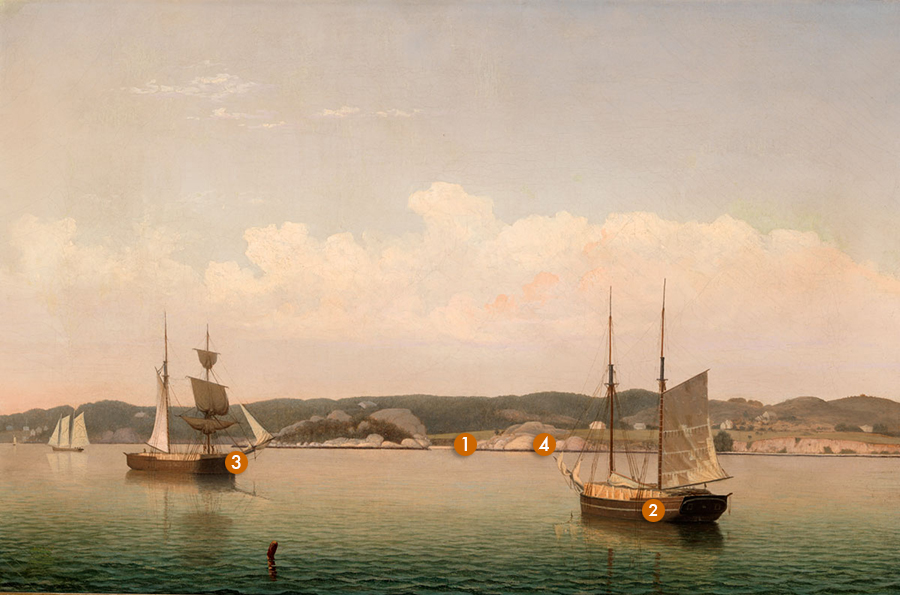An online project under the direction of the CAPE ANN MUSEUM
Stage Rocks and the western shore of Gloucester’s Outer Harbor (now Stage Fort Park) were only a quick walk west from town over the Blynman "Cut" (Canal) and, even in Lane’s day, were a quiet counterpoint to the constant activity of the inner harbor. The shoreline is dominated by huge granite outcroppings, their round tops worn smooth by the last glacier.
Lane did a detailed drawing of this shore in 1857 (Western Shore of Gloucester Outer Harbor, 1857 (inv. 107)), probably from the end of Fort Point, though possibly from a boat just offshore (see map). According to the inscription on this drawing, it was made for Harriet Davis, whose descendants gave it to the Cape Ann Museum in 1932. Lane did at least one other painting we know of from the drawing: Stage Rocks and Western Shore of Gloucester Outer Harbor, 1857 (inv. 348).
The area behind Stage Rocks is relatively flat and was the site of the first settlement of the Massachusetts Bay Colony in 1623. Fourteen men of the Dorchester Company settled here (on what was then called Fishermen's Field) and tried to survive through a combination of fishing and farming. They were successful at neither.
In 1626, under the leadership of Roger Conant, they moved on and established a village to the south near an ancient Native American trading center. They called the village Naumkeag, but three years later, it was incorporated as the Town of Salem.
Lane's painting of this important site shows a slightly narrower view than the drawing or the other painting. A lumber schooner and brig lie in the harbor, likely down from Maine on their way to Boston or further south. Gloucester Harbor was a popular stopover for vessels coming from Maine or Canada, whether to avoid weather or take on supplies, which is why the harbor was always full of a great variety of boats.
In a letter from Lane to Joseph Stevens, he wrote:
I yesterday made a sketch of Stage Fort and the surrounding scenery from the water. Piper has given me an order for a picture from this point of view to be treated as a sunset. I shall try to make something out of it but it will take some management as there is no foreground but water and vessels.
The above excerpt likely refers to the sunset view painted for John S. Piper (Stage Rocks and Western Shore of Gloucester Outer Harbor, 1857 (inv. 348)), but this work was done from the same drawing and deals with the same issue of “no foreground but water and vessels." Lane solved the problem by creating an intense pattern of wave shadow and reflection in the foreground, receding to flat water in the distance. The vessels are placed on a near diagonal facing each other, which compresses the view and focuses the eye on the granite domes on the shore and the white arc of Half Moon Beach between them. Lane has subtly alternated light and shadow on the hills and rocks in the distance, creating a rhythm corresponding with the outcroppings and recesses of the shoreline.
Stage Rocks and the Western Shore of Gloucester Outer Harbor is one of the rare paintings where Lane painted a bright midday light as opposed to the richer morning or evening light he preferred. The feeling of humidity and limpid stillness is accentuated by the tension of the nearly but not perfectly diagonal path of the vessels, which, if they were moving, would set them on a collision course. They feel heavy and torpid, locked in a perfect static tension. A strange green light pervades the scene, overlaid with pink tones on the horizon and rocks. There is an overall surreal quality to the moment—a compressed airlessness as though before a thunderstorm—that makes this work an unexpected masterpiece in Lane’s oeuvre.
– Sam Holdsworth
- Subject Types
: - Vessel Types
: - Cape Ann Locales
:
Historical Materials
Letter
Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive, Gloucester, Mass.
". . . will fully appreciate all that I have done in my garden, in ornamenting it, with flowers and plants, Rustic Arbours and Statues, and I only wish that you could be here to witness and enjoy his [Dr. J. L. Stevens] expressions of delight and interest, when a new flower attracts his attention, or some beauty of arrangement meets his eye. Samuel [B. Stevens of Castine] he tells me came up with the expectation of going on a voyage to Australia, but when he arrived in Boston he found the vessel with her compliment of men, and it is very uncertain if he goes in her. Your Mother and all at home are well. I yesterday made a sketch of Stage Fort and the surrounding scenery, from the water. Piper has given me an order for a picture from this point of view, to be treated as a sunset. I shall try to make something out of it, but it will require some management, as there is no foreground but water and vessels. One o’clock, it is very hot, the glass indicates 84° in my room, with the windows all open and a light breeze from the east, this is the warmest day . . .
. . . than devoting it to you. Since writing you last I have painted but one picture worth talking about and that one I intend for you if you should be pleased with it. It is a View of the beach between Stage Fort and Steep bank including Hovey’s Hill and residence, Fresh water cove and the point of land with the lone pine tree. Fessenden’s house, likewise comes into the picture. The effect is a mid day light with a cloudy sky, a patch of sunlight is thrown across the beach and the breaking waves, an old vessel lies stranded on the beach with two or three figures, there are a few vessels in the distance and the Field rocks likewise show at the left of the picture. I think you will be pleased with this picture, for it is a very picturesque scene especially the beach, as there are many rocks which come in to destroy the monotony of a plain sand beach, and I have so arranged the light and shade that the effect I think is very good indeed, however you will be better able to judge of that when you see it, the size is 20 x 33. . ."
Gloucester Outer Harbor served as a staging area for deep draft or heavily laden vessels waiting to come into the wharves in the shallow Old Harbor at high tide, or waiting to discharge cargo into smaller vessels. While Lane's paintings typically show one or two vessels in the harbor, works by other artists from the period, as well as contemporary descriptions, demonstrate that the harbor was usually crowded with vessels, especially in bad weather. The Outer Harbor could accommodate as many as three hundred vessels when they needed to shelter during a storm.
There were two deep spots where they could wait, the "Deep Hole" between Ten Pound Island and the Fort; and the "Pancake Grounds" between Ten Pound Island and Eastern Point. The "Pancake Grounds" also served as a quarantine area for ships arriving from foreign ports. "Deep Hole" was named for the (relatively) deep water between Rocky Neck and Fort Point to the Outer Harbor. Deeply loaded vessels had to anchor there for “lightering” (partial unloading by boats called “lighters”) prior to final unloading at wharfside. "Deep Hole" was 20–25 feet deep at low tide, when Harbor Cove was only 1–6 feet deep with bare ground around some wharves. "Deep Hole" is where you see ships anchored in Gloucester Harbor from Rocky Neck, 1844 (inv. 14), The Old Fort and Ten Pound Island, Gloucester, 1850s (inv. 30), , Gloucester Inner Harbor, 1850 (inv. 240), The Fort and Ten Pound Island, Gloucester, Massachusetts, 1847 (inv. 271), and Gloucester Harbor, 1848 (inv. 335) (which is coming to anchor).
The term "Deep Hole" is apparently a post-Bellum term. Prior to that, it was known as "The Stream" and, as later, served as anchorage where deeply loaded vessels could be lightered prior to docking in Harbor Cove. Alfred Mansfield Brooks in his book Gloucester Recollected uses this term on page 53. After the Civil War, merchant shipping in Gloucester was dominated by salt ships and later coal carriers, bringing a whole new culture to the harbor, and with it new names for old places.
John Heywood Photo for Hervey Friend
Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive (2013.068)
Schooners anchored on the Pancake Ground, taken from from Wonson's Cove, easterly side of the Rocky Neck causeway. Eastern Point Fort and garrison in background to far left.
Also filed under: Eastern Point »
c.1870 Stereograph card Procter Brothers, Publisher Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive
"Gloucester Harbor from Rocky Neck, Looking Southwest. This gives a portion of the Harbor lying between Ten Pound Island and Eastern Point. At the time of taking this picture the wind was from the northeast, and a large fleet of fishing and other vessels were in the harbor. In the range of the picture about one hundred vessels were at anchor. In the small Cove in the foreground quite a number of dories are moored. Eastern Point appears on the left in the background."
Southeast Harbor was known for being a safe harbor.
Also filed under: Historic Photographs » // Rocky Neck » // Schooner (Fishing) » // Small Craft – Wherries, and Dories »
Collection of Erik Ronnberg
View related catalogue entries (2) »
Also filed under: Dolliver's Neck » // Fresh Water Cove » // Gloucester Harbor, Inner / Harbor Cove » // Maps »
c.1870 Stereograph card Procter Brothers, Publisher Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive
View from Civil War fort on Eastern Point.
Also filed under: Eastern Point » // Historic Photographs »
44 x 34 in.
Henry Francis Walling, Map of the Towns of Gloucester and Rockport, Essex Co. Massachusetts. Philadelphia, A. Kollner, 1851
Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive
"Map of the Towns of Gloucester and Rockport, Massachusetts. H.F. Walling, Civil Engineer. John Hanson, Publisher. 1851. Population of Gloucester in 1850: 7,805. Population of Rockport in 1850: 3,213."
Also filed under: Annisquam River » // Brookbank » // Dolliver's Neck » // Fresh Water Cove » // Maps » // Norman's Woe » // Stage Rocks / Stage Fort / Stage Head » // Steepbank » // West Gloucester – Little River » // Western Shore »
Newsprint
Cape Ann Advertiser
Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive
Notice in the Cape Ann Advertiser announcing arrival of ships into the port of Gloucester, with details of their cargo.
Also filed under: Newspaper / Journal Articles » // Trade Routes and Statistics »
Newspaper
"Lane's studio seldom presents so many attractions to visitors as at the present time. With unwonted rapidity his easel has turned off pictures in answer to the numerous orders which have poured in from all quarters."
Also filed under: Chronology » // Newspaper / Journal Articles » // Studio Descriptions »
Electrotype impression
Collection of Erik Ronnberg
Also filed under: Gloucester Harbor, Inner / Harbor Cove » // Maps »
c.1870 Stereograph card Procter Brothers, Publisher Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive
Also filed under: Historic Photographs » // Stage Rocks / Stage Fort / Stage Head »
Pencil and ink on paper
15 x 22 1/8 in.
Cape Ann Museum, Gloucester, Mass., Gift of Mr. Donald K. Usher, in memory of Mrs. Margaret Campbell Usher, 1984 (2401.19)
Also filed under: Beacons / Monuments / Spindles » // Mackerel Fishing »
Watercolor on paper
8 3/4 x 19 3/4 in.
Cape Ann Museum, Gloucester, Mass., Gift of Rev. and Mrs. A. A. Madsen, 1950
Accession # 1468
Fishing schooners in Gloucester's outer harbor, probably riding out bad weather.
Also filed under: Elwell, D. Jerome » // Schooner (Fishing) »
Half Moon Beach is a small crescent of sand, nestled into Stage Fort Park, between Stage Point (where the remains of a Revolutionary War earthworks fort still stands) and a large ledge outcropping that on the far side houses the tablet commemorating the original 1623 settlement of the area by the Dorchester Company. At the time Lane painted his views of the Harbor in which one can see this beach, the entire little peninsula, once known as Fisherman's Field, was probably owned by the B. K. Hough family. The area, including this beach, is now public. From the beach, one can see much of the Outer Harbor, Pavilion Beach, and Ten Pound Island.
– Sarah Dunlap (June, 2015)
c.1870 Stereograph card Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive
Also filed under: Historic Photographs » // Stage Rocks / Stage Fort / Stage Head » // Western Shore »
c.1870 Stereograph card Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive
Also filed under: Historic Photographs »
Newspaper
"Mr. Lane has just completed a third picture of the Western Shore of Gloucester Harbor, including the distance from 'Norman's Woe Rock' to 'Half Moon Beach.' It was painted for Mr. William E. Coffin of Boston, and will be on exhibition at the artist's rooms for only a few days; we advise all our readers who admire works of art, and would see one of the best pictures Mr. Lane has ever executed..."
"...solitary pine, so many years a familiar object and landmark to the fisherman."
c.1870 Stereograph card Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive
Also filed under: Gloucester – City Views » // Historic Photographs » // Stage Rocks / Stage Fort / Stage Head » // Steepbank »
29 x 25 in.
Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive (#089)
Ernest Bowditch was a landscape gardener. This map shows some of the various names of landmarks around Stage Rocks.
Also filed under: Field Beach / Crescent (or Cressy's) Beach / Long Beach » // Maps » // Stage Rocks / Stage Fort / Stage Head »
The Stage, as it was known in Lane’s time, now Stage Fort Park, rises from the western shore of the Outer Harbor, just south and west of the Cut and the Blynman Bridge as you leave Gloucester. This was the first settlement of the Massachusetts Bay Colony in 1623 where fourteen men of the Dorchester Company landed and tried in vain to settle and survive through a combination of fishing and farming. They were successful at neither, and in 1626 they moved on and founded Salem.
During the Revolution the Gloucester patriots built a fort on the north side of Half Moon Beach to defend against British invaders which was never needed. The fort was restored for the War of 1812 and again for the Civil War, but again saw no action.
During Lane’s lifetime this area was the Hough farm. Townspeople were generally given free run of the place for strolling and picnics overlooking the harbor. The enormous rounded boulders and ledge outcroppings rose dramatically from the fields above the harbor without the tree cover that partially obscures them today.
Lane did numerous paintings of this area, including many views looking westward from the vantage point onboard a boat in the harbor. In Stage Rocks and the Western Shore of Gloucester Outer Harbor, 1857 (inv. 8) the Stage Rocks frame the west side of Gloucester Harbor and provided a peaceful and bucolic counterpoint to the intense activity of the city waterfront only a mile away across the harbor. Lane also painted the Stage Rocks from the beach just to the north near the Cut and Field Beach, which is on the southern side of the Stage Rocks facing out the harbor entrance to the sea.
Commonwealth of Massachusetts: Southern Essex District Registry of Deeds
1543 plan 0141_0002
The third of the three plans has the references on it. "Plan showing the taking of land, flats and beach for Stage Fort Park…1898..."
Includes a reference to the home of Mary Turnbull which is Steepbank.
Also filed under: Maps » // Steepbank »
c.1870 Stereograph card Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive
Also filed under: Gloucester – City Views » // Half Moon Beach » // Historic Photographs » // Steepbank »
44 x 34 in.
Henry Francis Walling, Map of the Towns of Gloucester and Rockport, Essex Co. Massachusetts. Philadelphia, A. Kollner, 1851
Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive
"Map of the Towns of Gloucester and Rockport, Massachusetts. H.F. Walling, Civil Engineer. John Hanson, Publisher. 1851. Population of Gloucester in 1850: 7,805. Population of Rockport in 1850: 3,213."
Also filed under: Annisquam River » // Brookbank » // Dolliver's Neck » // Fresh Water Cove » // Gloucester Harbor, Outer » // Maps » // Norman's Woe » // Steepbank » // West Gloucester – Little River » // Western Shore »
c.1870 Stereograph card Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive
Also filed under: Half Moon Beach » // Historic Photographs » // Western Shore »
c.1870 Stereograph card Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive
Also filed under: Gloucester – City Views » // Historic Photographs »
c.1890 Stereograph card Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive
"In the foreground is a clear sheet of water which washes upon the beach beyond. The Pavilion is quite prominent, while upon the rising background can be seen the steeples of the several churchs, the tower of the first Town House, and the Collins School House."
Also filed under: Gloucester – City Views » // Historic Photographs » // Pavilion Hotel »
Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive
Stage Fort from Hough's Farm, showing a panorama of the harbor from Pavilion Beach to Fort Point and Rocky Neck.
Also filed under: Field Beach / Crescent (or Cressy's) Beach / Long Beach »
c.1870 Stereograph card Procter Brothers, Publisher Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive
Also filed under: Gloucester Harbor, Outer » // Historic Photographs »
Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Southern Essex District Registry of Deeds. 1543 plan 0141_0003
salemdeeds.com
The third of the three plans has the references on it “Plan showing the taking of land, flats and beach for Stage Fort Park…1898…"
Includes a reference to the home of “Mary Turnbull” which is Steepbank.
Also filed under: Maps »
Commonwealth of Massachusetts: Southern Essex District Registry of Deeds
1543 plan 0141_0001
The third of the three plans has the references on it “Plan showing the taking of land, flats and beach for Stage Fort Park…1898…”
Includes a reference to the home of Mary Turnbull which is Steepbank.
Also filed under: Field Beach / Crescent (or Cressy's) Beach / Long Beach » // Maps » // Steepbank »
Colored lithograph
Cape Ann Museum Library and Archive
Also filed under: Western Shore »
29 x 25 in.
Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive (#089)
Ernest Bowditch was a landscape gardener. This map shows some of the various names of landmarks around Stage Rocks.
Also filed under: Field Beach / Crescent (or Cressy's) Beach / Long Beach » // Half Moon Beach » // Maps »
The Western Shore of Gloucester Harbor is characterized by the huge smooth glaciated boulders and granite outcroppings known as Stage Rocks, and the steep cliffs which separate Dolliver's Neck, Half Moon Beach, and Fresh Water Cove from the rolling fields beyond. The area was a quiet bucolic scene as portrayed by Lane in several paintings and drawings, in contrast to the bustling Inner Harbor. The shore is punctuated by the steep crags surrounding Rafe's Chasm and Norman's Woe at the southern end.
c.1870 Stereograph card Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive
Also filed under: Half Moon Beach » // Historic Photographs » // Stage Rocks / Stage Fort / Stage Head »
Colored lithograph
Cape Ann Museum Library and Archive
Also filed under: Stage Rocks / Stage Fort / Stage Head »
44 x 34 in.
Henry Francis Walling, Map of the Towns of Gloucester and Rockport, Essex Co. Massachusetts. Philadelphia, A. Kollner, 1851
Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive
"Map of the Towns of Gloucester and Rockport, Massachusetts. H.F. Walling, Civil Engineer. John Hanson, Publisher. 1851. Population of Gloucester in 1850: 7,805. Population of Rockport in 1850: 3,213."
Also filed under: Annisquam River » // Brookbank » // Dolliver's Neck » // Fresh Water Cove » // Gloucester Harbor, Outer » // Maps » // Norman's Woe » // Stage Rocks / Stage Fort / Stage Head » // Steepbank » // West Gloucester – Little River »
1851 44 x 34 in. Henry Francis Walling, Map of the Towns of Gloucester and Rockport, Essex Co. Massachusetts. Philadelphia, A. Kollner, 1851 Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive
"Map of the Towns of Gloucester and Rockport, Massachusetts. H.F. Walling, Civil Engineer. John Hanson, Printer. 1851. Population of Gloucester in 1850 7,805. Population of Rockport in 1850 3,213."
Also filed under: Baptist Church (Old, First, 1830) (Pleasant Street) » // Burnham Brothers Marine Railway » // Duncan's Point » // Five Pound Island » // Flake Yard » // Gloucester Harbor, Inner / Harbor Cove » // Harbor Methodist Church (Prospect Street) » // Low (Frederick G.) wharves » // Pavilion Hotel » // Procter Brothers » // Ropewalk » // Vincent's Cove »
Hermaphrodite brigs—more commonly called half-brigs by American seamen and merchants—were square-rigged only on the fore mast, the main mast being rigged with a spanker and a gaff-topsail. Staysails were often set between the fore and main masts, there being no gaff-rigged sail on the fore mast. (1)
The half-brig was the most common brig type used in the coasting trade and appears often in Lane’s coastal and harbor scenes. The type was further identified by the cargo it carried, if it was conspicuously limited to a specialized trade. Lumber brigs (see Shipping in Down East Waters, 1854 (inv. 212) and View of Southwest Harbor, Maine: Entrance to Somes Sound, 1852 (inv. 260)) and hay brigs (see Lighthouse at Camden, Maine, 1851 (inv. 320)) were recognizable by their conspicuous deck loads. Whaling brigs were easily distinguished by their whaleboats carried on side davits (see ). (2)
– Erik Ronnberg
References:
1. M.H. Parry, et al., Aaak to Zumbra: A Dictionary of the World's Watercraft Newport News, VA: The Mariners’ Museum, 2000), 268, 274; and A Naval Encyclopaedia (L.R. Hamersly & Co., 1884. Reprint: Detroit, MI: Gale Research Company, 1971), 93, under "Brig-schooner."
2. W.H. Bunting, An Eye for the Coast (Gardiner, ME: Tilbury House: 1998), 52–54, 68–69; and W.H. Bunting, A Day's Work, part 1 (Gardiner, ME: Tilbury House: 1997), 52.
Schooners in Lane’s time were, with few exceptions, two-masted vessels carrying a fore-and-aft rig having one or two jibs, a fore staysail, gaff-rigged fore- and main sails, and often fore- and main topsails. One variant was the topsail schooner, which set a square topsail on the fore topmast. The hulls of both types were basically similar, their rigs having been chosen for sailing close to the wind. This was an advantage in the coastal trade, where entering confined ports required sailing into the wind and frequent tacking. The square topsail proved useful on longer coastwise voyages, the topsail providing a steadier motion in offshore swells, reducing wear and tear on canvas from the slatting of the fore-and-aft sails. (1)
Schooners of the types portrayed by Lane varied in size from 70 to 100 feet on deck. Their weight was never determined, and the term “tonnage” was a figure derived from a formula which assigned an approximation of hull volume for purposes of imposing duties (port taxes) on cargoes and other official levies. (2)
Crews of smaller schooners numbered three or four men. Larger schooners might carry four to six if a lengthy voyage was planned. The relative simplicity of the rig made sail handling much easier than on a square-rigged vessel. Schooner captains often owned shares in their vessels, but most schooners were majority-owned by land-based firms or by individuals who had the time and business connections to manage the tasks of acquiring and distributing the goods to be carried. (3)
Many schooners were informally “classified” by the nature of their work or the cargoes they carried, the terminology coined by their owners, agents, and crews—even sometimes by casual bystanders. In Lane’s lifetime, the following terms were commonly used for the schooner types he portrayed:
Coasting schooners: This is the most general term, applied to any merchant schooner carrying cargo from one coastal port to another along the United States coast (see Bar Island and Mt. Desert Mountains from Somes Settlement, 1850 (inv. 401), right foreground). (4)
Packet schooners: Like packet sloops, these vessels carried passengers and various higher-value goods to and from specific ports on regular schedules. They were generally better-maintained and finished than schooners carrying bulk cargoes (see The Old Fort and Ten Pound Island, Gloucester, 1850s (inv. 30), center; and Gloucester Inner Harbor, 1850 (inv. 240), stern view). (5)
Lumber schooners: Built for the most common specialized trade of Lane’s time, they were fitted with bow ports for loading lumber in their holds (see View of Southwest Harbor, Maine: Entrance to Somes Sound, 1852 (inv. 260)) and carried large deck loads as well (Stage Rocks and the Western Shore of Gloucester Outer Harbor, 1857 (inv. 8), right). Lumber schooners intended for long coastal trips were often rigged with square topsails on their fore masts (see Becalmed Off Halfway Rock, 1860 (inv. 344), left; ; and Lumber Schooner in a Gale, 1863 (inv. 552)). (6)
Schooners in other specialized trades. Some coasting schooners built for carrying varied cargoes would be used for, or converted to, special trades. This was true in the stone trade where stone schooners (like stone sloops) would be adapted for carrying stone from quarries to a coastal destination. A Lane depiction of a stone schooner is yet to be found. Marsh hay was a priority cargo for gundalows operating around salt marshes, and it is likely that some coasting schooners made a specialty of transporting this necessity for horses to urban ports which relied heavily on horses for transportation needs. Lane depicted at least two examples of hay schooners (see Gloucester Harbor, 1850s (inv. 391), left; and Coasting Schooner off Boon Island, c.1850 (inv. 564)), their decks neatly piled high with bales of hay, well secured with rope and tarpaulins.
– Erik Ronnberg
References:
1. Howard I. Chapelle, The History of American Sailing Ships (New York: W.W. Norton & Co., 1935), 258. While three-masted schooners were in use in Lane’s time, none have appeared in his surviving work; and Charles S. Morgan, “New England Coasting Schooners”, The American Neptune 23, no. 1 (DATE): 5–9, from an article which deals mostly with later and larger schooner types.
2. John Lyman, “Register Tonnage and its Measurement”, The American Neptune V, nos. 3–4 (DATE). American tonnage laws in force in Lane’s lifetime are discussed in no. 3, pp. 226–27 and no. 4, p. 322.
3. Ship Registers of the District of Gloucester, Massachusetts, 1789–1875 (Salem, MA: The Essex Institute, 1944). Vessels whose shipping or fishing voyages included visits to foreign ports were required to register with the Federal Customs agent at their home port. While the vessel’s trade or work was unrecorded, their owners and master were listed, in addition to registry dimensions and place where built. Records kept by the National Archives can be consulted for information on specific voyages and ports visited.
4. Howard I. Chapelle, The National Watercraft Collection (Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution, 1960), 40, 42–43.
5. Ibid., 42–43, 73.
6. Ibid., 74–76.
In R. H. Dana, The Seaman's Friend, 13th ed. (Thomas Groom & Co. Publisher, 1873)
A topsail schooner has no tops at her foremast, and is fore-and-aft rigged at her mainmast. She differs from an hermaphrodite brig in that she is not properly square-rigged at her foremast, having no top, and carrying a fore-and-aft foresail instead of a square foresail and a spencer.
Detail views: marine railway and hauling cradle for vessel Wood rails, metal rollers, chain; wood cradle. Scale: ½" = 1' (1:24) Original diorama components made, 1892; replacements made, 1993. Cape Ann Museum, from Gloucester Chamber of Commerce, 1925 (2014.071)
A schooner is shown hauled out on a cradle which travels over racks of rollers on a wood and metal track.
Also filed under: Burnham Brothers Marine Railway » // Marine Railways »
c. 1900 Glass plate negative Collection of Erik Ronnberg
Also filed under: Lobstering »
"The Maine Register for the Year 1855, embracing State and County Officers, and an abstract of the law and resolves; together with a complete business directory of the state, and a variety of useful information."
Details about Maine's lumber trade in 1855, see pp. 250–52
Also filed under: Castine » // Lumber Industry »
The timber trade played an important role in New England’s economy from Colonial days through the mid-19th century, supplying the vast quantities of lumber which a rapidly growing nation demanded. While Cape Ann’s woodlands were depleted early on, timber continued to be harvested from northern New England and the Maritime Provinces right up to the Civil War.
With a deep and safe harbor, Gloucester often served as a layover spot where vessels bound from Maine to Boston, New York or Baltimore and heavily laden with lumber could ride out bad weather. Because of this, Fitz Henry Lane’s paintings of Gloucester Harbor often show a schooner or a brig, loads of lumber clearly visible on their decks, sheltering along the Western Shore.
References:
Honey, Mark E., "King Pine, Queen Spruce, Jack Tar," An Intimate History of Lumbering on the Union River, Volumes 1-5. This source, in its entirety, lays down the foundation of Downeast Maine's unique culture which was built upon pine lumber and timber, the cod fisheries, coasting, shipbuilding, and the interrelationships of family and community.
1852 Photograph
Also filed under: Schooner (Coasting / Lumber / Topsail / Packet / Marsh Hay) »
Advertisement for The Bangor News Company, est. January 31, 1881 Castine Historical Society Collections (2008.02)
Also filed under: Historic Photographs »
"The Maine Register for the Year 1855, embracing State and County Officers, and an abstract of the law and resolves; together with a complete business directory of the state, and a variety of useful information."
Details about Maine's lumber trade in 1855, see pp. 250–52
Also filed under: Castine » // Schooner (Coasting / Lumber / Topsail / Packet / Marsh Hay) »
Based on the will of Catalina Davis, Lane made a painting for Harriet Phena (Mason) Davis (1823–74). She was the third wife of William Fuller Davis (they were married in 1853) and the mother of Catalina Davis, and is said to have studied painting with Fitz Henry Lane. Her husband, William Fuller Davis (1809–84) earned his way in life as a sailmaker and later as a fish merchant, maintaining warehouses and wharves in Gloucester's Fort district. The Davises moved into a large house a few blocks up from Gloucester Harbor. In addition to Stage Rocks and the Western Shore of Gloucester Outer Harbor, 1857 (inv. 8) which was given to the Cape Ann Museum by the Davises' youngest daughter, Catalina, the family also owned one of Lane's views of Owl's Head, Maine.