An online project under the direction of the CAPE ANN MUSEUM
Historical Materials: Vessel Types
Historical Materials » Vessel Types » Small Craft – Wherries, and Dories
You have navigated to this pages from catalog entry: View of the Town of Gloucester, Mass., 1836 (inv. 437)
Small Craft – Wherries, and Dories
View related Fitz Henry Lane catalog entries (28) »
The term “wherry”—variously spelled—has a long history with many hull types, some dating from the fifteenth century. (1) The version known to Lane appears to be a variant of the dory hull form and probably was developed by French and English fishermen in the Newfoundland fisheries before 1700. (2) From that time, the wherry and the dory co-evolved, their similarities the result of their construction, their differences the result of use. By the early nineteenth century, their forms reached their final states, if fragments of contemporary descriptions are any indication. (3)
By the time Lane was depicting wherries, the type (as used for fishing) resembled a larger, wider version of a dory. The extra width was due to greater bottom width (both types had flat bottoms), with a wider transom at the stern instead of the narrow, v-shaped “tombstone.” These features are easy to see in one of his drawings (see Three Men, One in a Wherry (inv. 225)) and a painting (see Sunrise through Mist, 1852 (inv. 98)), the latter depicted alongside a dory, clearly showing the differences.
No published descriptions of the uses of wherries on Cape Ann in Lane’s time have come to light, but an example in broadside view offers one use. In Becalmed Off Halfway Rock, 1860 (inv. 344), a pinky (in right foreground) has a dory and a wherry in tow, the latter loaded with a gill net for catching mackerel. (4) The greater size of the wherry is required for stowing the net, as well as setting it while the dory tows away one end to set it in way of the mackerel school.
In Lane’s time, wherries would have been used where bulky gear was called for in the coastal fisheries, i.e. gill nets, and fish traps such as pound nets, fyke nets, and lobster traps. Migrating fish schools (herring, mackerel) and shellfish were the target species.
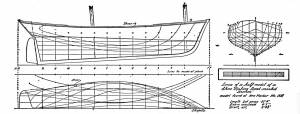
The dory’s development was first dictated by its use in shore fishing, where small size and light weight made it easy to maneuver around rocks and shallows, and to haul ashore at the end of a day’s work. Its simple design made it easy and cheap to build. This is borne out by the standardized construction and sizes used by Simon Lowell’s boat shop at Salisbury Point, Massachusetts at the turn of the nineteenth century. Lowell called his boats “wherries,” but in Swampscott, Massachusetts, the fishermen, who used them called them “dories,” which may mark the beginning of the latter term’s wider use. (5)
The dories we see in Lane’s paintings are in virtually every way like the ones we know today. One of the best examples (see View from Kettle Cove, Manchester-by-the-Sea, 1847 (inv. 94)) even shows interior detail, including frames, leaving no doubt about its construction. Other good examples are found in Salem Harbor, 1853 (inv. 53), View of Gloucester Harbor, 1848 (inv. 97), and Sunrise through Mist, 1852 (inv. 98).
For inshore fishing, dories were used to catch mackerel and herring, either with hook and line or with small nets. Hooks and line were used for flat fish (flounder, dab, and fluke), rock cod, hake, and cunner. Eels were speared (see View from Kettle Cove, Manchester-by-the-Sea, 1847 (inv. 94)), clams were dug, and lobsters trapped. In Lane’s later years, the use of dories in trawling (setting long “trawl lines” with many baited hooks) was in its earliest. This method required six to ten dories carried on board a schooner to fish on the distant banks off New England and Canada. Early records of dory trawling in New England are fragmentary, giving the mid-1840s as the time of introduction. (6) The Gloucester-owned schooner "Anna" made a successful dory trawling trip to the Grand Banks in 1854, but no depiction of this vessel by Lane has been found or recorded. (5) Despite successful early efforts, dory trawling from Gloucester was slow to be accepted, and the fishery had very limited growth prior to 1860. (7)
– Erik Ronnberg
References:
1. M.H. Parry et al., Aak to Zumbra (Newport News, VA: The Mariners’ Museum, 2000), 634.
2. John Gardner, The Dory Book (Camden, ME: International Marine Publishing Company, 1978), 5–9.
3. Ibid., 25–29.
4. John Wilmerding, ed., Paintings by Fitz Hugh Lane (Washington, DC: National Gallery of Art, 1988), 89, 92. The “possibly discarded whaleboat” is definitely a wherry.
5. Gardner, 9, 10.
6. Wesley George Pierce, Goin’ Fishin’ (Salem, MA: Marine Research Society, 1934), 63–64.
7. Raymond McFarland, A History of New England Fisheries (Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania, 1911), 279.
Related tables: "General Gates" (New England Boat; Casco Bay Boat) »
Stereograph card
Procter Brothers, Publisher
Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive
"Gloucester Harbor from Rocky Neck, Looking Southwest. This gives a portion of the Harbor lying between Ten Pound Island and Eastern Point. At the time of taking this picture the wind was from the northeast, and a large fleet of fishing and other vessels were in the harbor. In the range of the picture about one hundred vessels were at anchor. In the small Cove in the foreground quite a number of dories are moored. Eastern Point appears on the left in the background."
Southeast Harbor was known for being a safe harbor.
Also filed under: Gloucester Harbor, Outer » // Historic Photographs » // Rocky Neck » // Schooner (Fishing) »
Also filed under: Chebacco Boat / Dogbody / Pinky » // Ship Models »
Gloucester, MA
4 x 33 1/2 x 7 1/4 in (10.16 x 85.09 x 18.415 cm)
Peabody Essex Museum
Also filed under: Objects » // Ship Models »