An online project under the direction of the CAPE ANN MUSEUM
Historical Materials: Maritime & Other Industries & Facilities
Historical Materials » Maritime & Other Industries & Facilities » Hand-lining
You have navigated to this pages from catalog entry: Gloucester Harbor, 1847 (inv. 23)
Hand-lining
View related Fitz Henry Lane catalog entries (9) »
"Hand-lining" was fishing with a single line which had one or sometimes two hooks, as opposed to "trawling," in which a single line had many hooks. Hand-lining was the exclusive American fishing method from colonial times to the mid-19th century, and continued in use, taking second place to dory trawling only after the Civil War. Even then, it persisted into the twentieth century for some offshore fishing grounds, while hand-lining from dories remained a favored method for the shore fisheries.
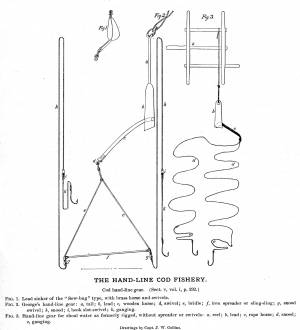
Hand-line fishing on the offshore banks was done in relatively shallow water (10 to 45 fathoms), often over rocky bottom. This method depended on catching fish at mid-levels as well as on the bottom, hence the lines were relatively short, seldom longer than 75 fathoms. Each fisherman worked two lines, fishing from the schooner's rail. Bait could be salted clams, fresh-caught squid, and even birds.
Hand-lining by American schooners on the Grand Banks declined in the 1830s as they turned to Georges Bank to exploit that neglected resource. In doing so, they turned to a highly modified hand-lining gear using two hooks on a single line. The hooks were on a pair of long gangings (leaders), joined at the sinker and spread apart 12 to 18 inches by a metal rod (or wooden spreader) called a "sling ding." The hand-line itself was much longer - as much as 900 feet, allowing the gear to cover a broad area over a shallow sandy bottom with few obstructions.
On Georges Bank, the schooners anchored where the wind would set the vessels broadside to tidal currents, with the crew fishing from the down-current side. This allowed the lines to be paid out without getting tangled with each other or bunching up astern. The long hand-lines, combined with heavy sinkers and (hopefully) two large cod on the hooks made for strenuous hauling, made all the more so by the tidal current. Georges fishermen were regarded as the strongest in the Cape Ann fisheries.
The wealth of resources and the proximity of Georges Bank was offset by its hazards in heavy weather, as many of Gloucester's widows could testify. Breaking shallows, mountainous waves and winter storms took their toll, but this danger was compounded when numerous vessels anchored within sight of each other. A parted anchor cable could send a vessel crashing into another with the loss of both with their crews.
Related tables: Fishing » // Waterfront, Gloucester »
Steel engraving after drawing in G. Brown Goode, The Fisheries and Fishery Industries of the United States (Washington, DC: Government Printing Office)
8 1/2 x 11 in. (page size)
Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive, Gloucester, Mass.
See pl. 31.
Shows the two basic types of hand-line gear in use in mid-ninteenth century. At left is the Georges gear, developed for fishing on Georges Bank. At right is shoal water gear, as commonly used in the inshore fisheries using dories and other small craft. The spreader, or "sling-ding" was used on this type of gear with the advent of dory hand-lining on offshore grounds.
Also filed under: Cod / Cod Fishing »
Steel engraving after drawing in G. Brown Goode, The Fisheries and Fishery Industries of the United States (Washington, DC: Government Printing Office, 1883)
8 1/2 x 11 in. (page size)
Cape Ann Museum Library & Archive, Gloucester, Mass.
See pl. 32.
Also filed under: Cod / Cod Fishing » // Georges Bank, Mass. »
Model made for marine artist Thomas M. Hoyne
scale: 3/8" = 1'
Thomas M. Hoyne Collection, Mystic Seaport, Conn.
While this model was built to represent a typical Marblehead fishing schooner of the early nineteenth century, it has the basic characteristics of other banks fishing schooners of that region and period: a sharper bow below the waterline and a generally more sea-kindly hull form, a high quarter deck, and a yawl-boat on stern davits.
The simple schooner rig could be fitted with a fore topmast and square topsail for making winter trading voyages to the West Indies. The yawl boat was often put ashore and a "moses boat" shipped on the stern davits for bringing barrels of rum and molasses from a beach to the schooner.
– Erik Ronnberg
References:
Jeffrey Bolster, Black Jacks: African American Seafarers in the Age of Sail (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1997).
Howard I. Chapelle, American Small Sailing Craft (New York: W.W. Norton & Co., 1951), 29–31.
Also filed under: Schooner (Fishing) » // Ship Models »